Southeast Asia (SEA) finds itself at a crucial juncture in the journey towards electric vehicle (EV) production and adoption as the world transitions towards sustainable transportation solutions. The region has several significant keys for developing the EV industry, such as Indonesia's nickel supply and Thailand's EV manufacturing potential. However, the ASEAN EV industry faces many challenges and threats that must be overcome to ensure success in the region.
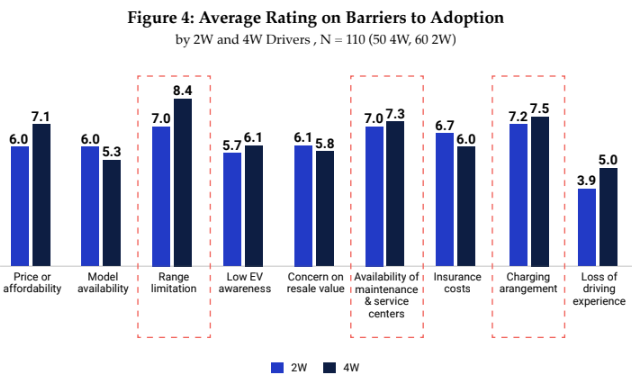
Image Source: YCP White Paper
Among the foremost concerns hindering widespread EV adoption in SEA is range anxiety – the fear of running out of power before reaching the next charging station. This psychological barrier, rooted in perceptions of older EV models, underscores the urgent need for comprehensive customer education on factors influencing range and dispelling misconceptions.
Providing adequate charging infrastructure remains a critical challenge, particularly in rural and remote areas with limited accessibility. Urgent expansion efforts are needed to meet the growing demand for EVs in the SEA market, as outlined by ambitious targets set by regulatory bodies. Investment in charging infrastructure is paramount to fostering consumer confidence and accelerating EV adoption.
Inadequate service and repair facilities pose a significant hurdle for EV owners, especially in ensuring the proper maintenance of battery packs. The scarcity of trained mechanics and widespread networks of service centers undermines the reliability and convenience of EV ownership. Addressing this challenge requires concerted efforts to enhance service infrastructure and technician training programs.
While government support has narrowed the price gap between traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and EVs, affordability remains a key consumer consideration. Many are unaware of available incentives, highlighting the need for greater transparency and outreach efforts. Bridging this affordability gap is essential to making EVs accessible to a broader demographic.
Limited options in EV models compared to traditional ICE vehicles constrain consumer choice and market penetration. However, with the ramp-up of local EV and battery production, this challenge is expected to diminish over time. A diverse range of EV models catering to consumer preferences and needs is crucial for mass adoption.
Uncertainty surrounding EV resale value, limited availability, and range of older models, dampens market demand for used EVs. Overcoming these concerns requires a deeper understanding of battery lifespan, charging habits, and market dynamics. Building consumer confidence in the long-term value proposition of EVs is essential for fostering a thriving secondary market.
Insufficient historical data and repair knowledge for EVs contribute to higher insurance premiums, deterring potential buyers. However, as local production increases and repair knowledge disseminates, insurers may offer more competitive products for EV owners. Collaborative efforts between insurers, manufacturers, and regulatory bodies are essential for addressing risk factors and reducing insurance costs.
Lack of familiarity with EV technology, available models, and government incentives poses a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Investment in education and awareness campaigns is crucial for dispelling myths and misconceptions surrounding EVs. Empowering consumers with knowledge about EVs' environmental, economic, and social benefits is paramount for driving uptake in the region.
Source: https://ycpsolidiance.com/white-paper/electric-vehicle-powerhouse-thailand-sea

Digital Lending in Southeast Asia: Current Trends and Future Outlook
Digital lending in Southeast Asia (SEA) has been on an upward trajectory, significantly enhancing financial access for both individuals and businesses. The region's high internet and mobile penetration rates have facilitated this growth, enabling more people to access financial services conveniently. Governments across SEA are actively promoting digital lending as a means to improve financial inclusion, particularly for the underbanked and unbanked populations. For instance, digital lenders in countries like Indonesia and the Philippines have capitalized on the surge in internet usage to offer innovative lending solutions.

The Latest Trends and Developments in SEA’s Digital Payments Landscape
The adoption of digital payments in Southeast Asia (SEA) has accelerated, driven by technological advancements, government initiatives, and changing consumer behaviors. It has evolved from simple online transactions to sophisticated financial ecosystems that include various payment methods such as mobile wallets, QR code payments, and Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) options.

Navigating the Digital Era: Future Jobs and Skills in the Age of Digitalization
The job market's transformation driven by digitalization highlights the need to understand emerging trends and acquire essential skills for thriving.

Challenges to Entry and Success in Indonesia's Skincare Market
Entering and succeeding in Indonesia's skincare market presents many challenges and threats for businesses aiming to carve out a niche in this dynamic industry. From supply chain disruptions to regulatory hurdles and intense market competition, skincare companies must navigate various obstacles to establish a foothold and thrive in the Indonesian market.